Definition: Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)
Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM) is defined as alignment of strategic business goals of the organization with human resources, so as to foster innovation and improve motivation, satisfaction, productivity, and eventually overall performance. Strategic HRM is a relatively new term, which differentiates itself from traditional HRM which was just merely an organizational function.
Importance of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)
Since the last twenty years or so, there was an increasing fear of HR being secluded from business goals and as a separate part of the organizations. There was an increasing need felt across sectors of HR playing a vital role in improving productivity in organizations to achieve a competitive edge. So, strategic HRM came into existence. The primary goal of strategic human resource management is to solve business objectives or obstacles that may not occur within the direct purview of HRM. This has to be done through effective HRM itself. So it is basically tuning of human resource management (HRM) to suit business objectives. The other types of HRM are Hard HRM and Soft HRM.
For strategic HRM, there must be effective cooperation between the top management and the HR head. Some of the challenges faced in modern day HRM are as follows:
- Cross cultural issues and interaction
- Internationalization
- Changing ownership due to increased M & A
- Rapidly changing business environments
- Technological advancements
Elements of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)
The pillars for SHRM are:
a) Humans are not just resources but they are an asset to an organization, which should provide a competitive edge to the organization.
b) It’s the people within the organization who actually implement such change.
c) Every change is achievable only through a proper planning followed by execution with respect tpo the organizational needs and objectives.
d) The main aim of strategic HRM is to concentrate on the ways through which the firm can take an edge over its competitors.
e) According to Hendry and Pettigrew, SHRM has four different meanings, mainly:
- Making use of planning.
- Designing and managing people via a coherent approach.
- Developing systems which are based on employment policy and workforce strategy.
- Bringing out coordination between HR activities and other policies into developing business strategy.
- Considering people as resources and achieving competitive edge by making the best of them.
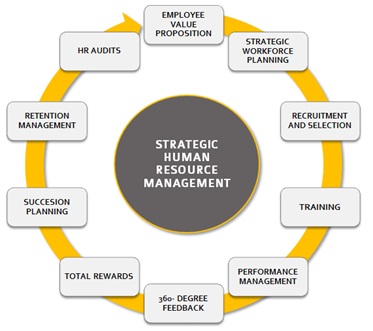
The above diagram shows the roles of SHRM
Objectives of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)
The main aim of strategic HRM is to address issues related to organizational culture, structure, effectiveness, resource matching, and performance. It involves developing the process capabilities as well as managing the human capital effectively. The approaches used in strategic HRM can be categorized into 5 categories mainly:
- Resource based Strategy: Addresses issues wherein the strategic capabilities of the firm can be increased.
- High Commitment Management: By enhancing the mutual commitment between the managers and their employees.
- High Involvement Management: Treating employees as their partners in the business.
- High Performance Management: Improves the performance of the firm by focusing on improving the productivity, growth and profitability rate of its people.
- Achieving Strategic Fit: Integration of human capital and resources is necessary for smooth and profitable operation of business.
Examples of Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)
- Infosys Chairman Mr. Narayan Murthy has emphasized on human capital as one of Infosys’ critical factors for growth. Thus, there has been a strategic Human resource dimension added to the organization in the form of ‘People managers’, whose function is to look after the needs of employees. The company aims to treats its employees as assets rather than just as resources. Nurturing and nourishing the resources ensures competitive advantage for Infosys. Thus, a dedicated human resource department including people managers in every group serves as a SHRM practice which fulfills the business objectives of the organization.
- Samson Enterprises through strategic HR initiatives started recruiting people with good communication skills along with technological prowess, due to the increase in number of client calls, so that client solutions could be effectively dealt with by the team.





